ANALYZING THE IMPACT OF SEPARATION OF POWERS: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF EXECUTIVE, LEGISLATURE, AND JUDICIARY
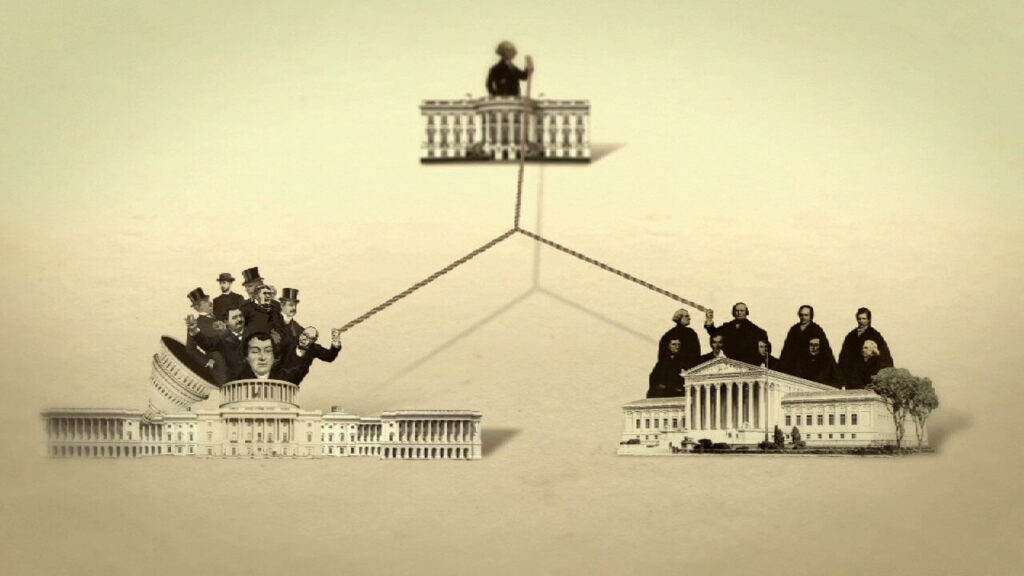
The separation of powers is a fundamental principle in democratic governance, aimed at preventing the concentration of power in a single authority. It divides governmental powers into distinct branches, typically the executive, legislature, and judiciary, each with separate functions and responsibilities. This article presents a comparative study that analyzes the impact of the separation of powers on these three branches. By examining their roles, interactions, and independence, we can gain insights into the functioning of democratic systems around the world.
- The Executive Branch:
The executive branch, led by the head of state or government, holds the responsibility for implementing and enforcing laws. It executes policies, manages public administration, and represents the nation domestically and internationally. The separation of powers limits executive authority and ensures accountability. By studying different countries, we can assess how the executive branch’s powers and checks and balances vary, influencing governance and decision-making.
- The Legislative Branch:
The legislature, composed of elected representatives, is responsible for making laws, approving budgets, and overseeing the executive branch’s actions. It serves as a voice for the people, representing their interests and providing a platform for debate and discussion. Comparative analysis of legislatures reveals the impact of their structure, composition, and relationship with the executive on lawmaking, policy formulation, and democratic representation.
- The Judicial Branch:
The judiciary acts as an impartial arbiter, interpreting laws and ensuring their compliance with constitutional principles. It safeguards the rights and freedoms of individuals, resolves disputes, and upholds the rule of law. Comparative studies shed light on the independence, competence, and integrity of the judiciary, examining its ability to check the powers of the executive and legislature, and to safeguard citizens’ rights.
- Interactions and Checks and Balances:
A key aspect of the separation of powers is the interplay and checks and balances among the three branches. Analyzing how these branches interact and oversee each other’s actions provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of the separation of powers. Comparative case studies can highlight successful mechanisms that foster cooperation, mitigate conflicts, and uphold democratic principles.
- Impact on Democracy and Governance:
By examining the impact of the separation of powers on executive, legislative, and judicial branches, we can evaluate its influence on democracy and governance. We can explore the degree of power concentration or diffusion, assess the responsiveness of institutions to public needs, and understand the overall functioning and stability of democratic systems.
Conclusion:
The separation of powers is a cornerstone of democratic governance, ensuring a system of checks and balances that prevents the abuse of power. Through a comparative study of the executive, legislature, and judiciary, we can assess the impact of this principle on democratic systems around the world. Understanding the strengths, weaknesses, and dynamics of these branches provides valuable insights for policymakers, scholars, and citizens seeking to strengthen democratic institutions and ensure effective governance.