THE IMPACT OF TRANSPORTATION PLANNING ON URBAN DESIGN
The Impact of Transportation Planning on Urban Design
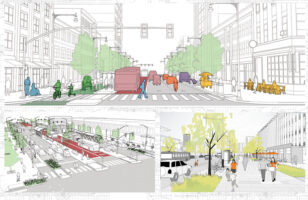
Transportation planning and urban design are intricately linked, influencing one another in profound ways. The choices made in transportation planning have a direct and lasting impact on the physical and social fabric of our cities. In this article, we will explore how transportation planning shapes urban design and why it’s crucial to consider the interplay between these two elements for sustainable and vibrant urban environments.
1. Mobility and Accessibility
Transportation planning significantly affects how people move within a city. The type and layout of transportation infrastructure, such as roads, public transit, and bike lanes, determine the mobility and accessibility of a city. A well-planned transportation system can enhance the accessibility of various areas, connecting residents to jobs, schools, and services more efficiently. Conversely, poor planning can lead to congestion, limited access, and social isolation.