WHAT IS COMPOSITE MASONRY | TYPE OF COMPOSITE MASONRY
What is Composite Masonry? A Comprehensive Overview
Composite masonry is a construction technique that combines different types of masonry units and materials to create a single, unified structure with enhanced performance characteristics. This innovative approach aims to leverage the strengths of various materials while mitigating their individual weaknesses, resulting in a more durable, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing outcome.
Key Characteristics of Composite Masonry
Composite masonry involves the strategic combination of two or more different materials, often traditional brick or concrete blocks, along with modern materials like reinforced concrete, steel, or even advanced composites. The integration of these materials brings forth several key characteristics:
- Strength and Durability: By merging materials with varying mechanical properties, composite masonry structures gain improved strength and durability compared to using a single material. This enhances the structure’s ability to withstand external forces, impacts, and environmental conditions.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Composite masonry allows designers to tailor the mix of materials to meet specific project requirements. This flexibility enhances the adaptability of structures to varied loads, functions, and site conditions.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The combination of different materials can result in visually striking designs that blend the best of both traditional and contemporary architectural styles. This can enhance the overall aesthetic appeal of the structure.
- Thermal Insulation: The incorporation of insulating materials into composite masonry can lead to improved thermal performance, contributing to energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
- Reduced Material Usage: Combining different materials strategically can lead to optimized use of resources, reducing the overall consumption of energy-intensive materials like concrete and steel.
Types of Composite Masonry
There are various types of composite masonry techniques, each with its unique approach to combining materials for specific benefits:
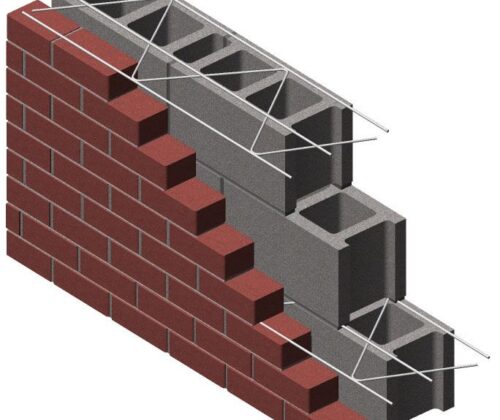
- Brick-Concrete Composite Masonry: This type integrates brick masonry with concrete, typically using bricks as the outer layer and concrete blocks as the inner core. The brick facade provides aesthetics, while the concrete core offers strength and load-bearing capacity.

- Stone-Reinforced Concrete Composite Masonry: Natural stone facades combined with reinforced concrete cores offer an amalgamation of traditional charm and modern robustness. This technique is often used in historical restoration and upscale architectural projects.
- Concrete Block-Steel Composite Masonry: Concrete blocks combined with steel elements like columns, beams, and reinforcement bars create structures with heightened load-bearing capabilities. Steel provides tensile strength, while concrete blocks offer compression strength.
- Composite Insulating Masonry: This approach involves mixing insulating materials like expanded polystyrene (EPS) beads or foam with traditional masonry units. The result is a lightweight yet thermally efficient structure ideal for energy-conscious construction.
- Fiber-Reinforced Composite Masonry: Incorporating fibers, such as glass or carbon fibers, into masonry materials enhances their tensile strength and crack resistance. This technique is particularly useful in earthquake-prone regions.
Benefits and Considerations
While composite masonry offers numerous advantages, it’s essential to consider certain factors:
Benefits:
- Enhanced Performance: Composite masonry structures exhibit improved strength, durability, and resistance to various forces and environmental factors.
- Design Flexibility: The technique allows architects and engineers to create unique designs while maintaining structural integrity.
- Resource Efficiency: Optimized material usage contributes to reduced environmental impact and resource consumption.
- Cost Savings: Combining materials strategically can lead to cost-effective solutions without compromising quality.
Considerations:
- Compatibility: Materials must be chosen carefully to ensure compatibility, preventing issues like differential movement or corrosion.
- Construction Expertise: Skilled craftsmanship is crucial for successfully implementing composite masonry due to the intricate nature of combining materials.
- Maintenance: Different materials may have distinct maintenance requirements, necessitating ongoing attention to preserve the structure’s integrity and appearance.
Conclusion
Composite masonry stands as a testament to the evolution of construction techniques, fusing tradition with innovation. By harnessing the strengths of diverse materials, structures can be created that not only withstand the test of time but also contribute to sustainable and aesthetically pleasing architectural landscapes. With careful planning, execution, and ongoing maintenance, composite masonry opens the door to a world of possibilities in modern construction.