UNDERSTANDING THE LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS: AN OVERVIEW OF THERMODYNAMICS-II
Understanding the Laws of Thermodynamics: An Overview of Thermodynamics-II
Thermodynamics is a fundamental branch of physics that deals with the principles governing the behavior of energy and matter. In our previous article, we introduced you to the basics of thermodynamics and discussed the four laws that form its foundation. In this article, we will delve deeper into the subject, exploring the second law and its implications.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a crucial pillar of this field, and it deals with the concept of entropy. Entropy is a measure of disorder or randomness in a system. This law, often summarized as “heat flows from hot to cold,” has several key points:
- The Irreversibility Principle: This principle asserts that natural processes tend to increase the overall entropy of the universe. In simpler terms, systems naturally evolve towards a state of greater disorder. This implies that once energy is converted into a less organized form, it cannot spontaneously return to its original state.
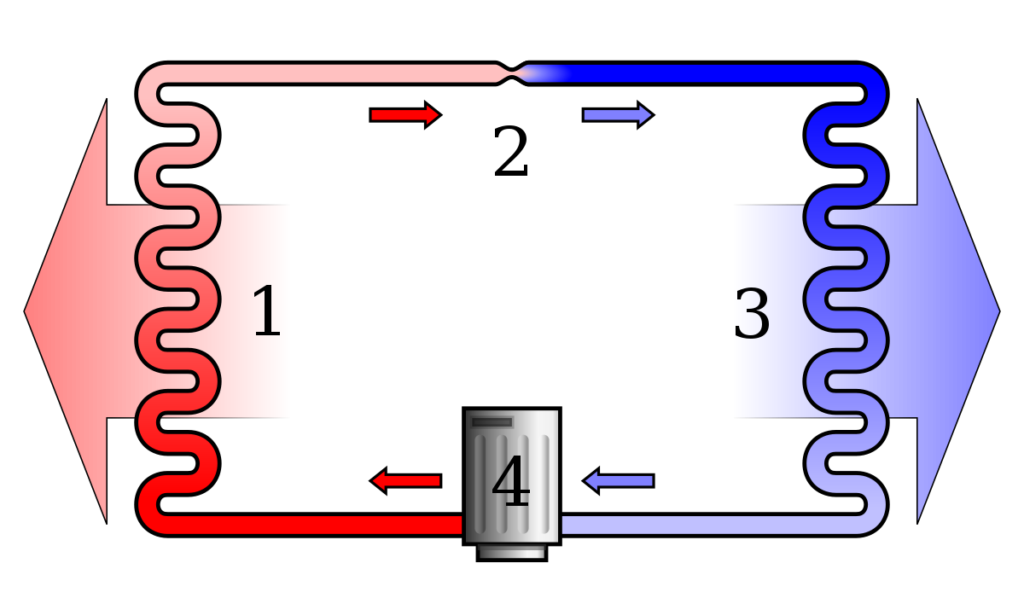
- Heat Transfer Direction: The second law defines the direction of heat transfer. Heat energy always flows from areas of higher temperature to areas of lower temperature. This is why your coffee cools down in a cold room, and not the other way around.
- Efficiency Limitations: The second law imposes a limit on the efficiency of heat engines, such as steam engines or car engines. No engine can be 100% efficient, as some of the energy input is always lost as waste heat. This is known as the Carnot efficiency.

Entropy and the Arrow of Time
Entropy is often associated with the “arrow of time.” As time progresses, the entropy of an isolated system will increase. This means that we can distinguish past from future based on the level of disorder in a system. For instance, if you see a video of a broken egg magically coming back together, you would immediately recognize it as fiction, as it violates the second law of thermodynamics.
Applications of the Second Law
Understanding the second law of thermodynamics is crucial in various fields:
- Engineering: Engineers use the second law to design efficient machines, refrigeration systems, and power plants. It helps in optimizing processes and minimizing energy waste.
- Chemistry: In chemical reactions, the second law is fundamental. It guides chemists in predicting whether a reaction will occur spontaneously or not.
- Biological Systems: Biological processes, such as metabolism, also follow the second law. Living organisms must continuously take in energy to maintain their internal order and counteract the tendency toward increasing entropy.

The Third Law of Thermodynamics
In addition to the second law, there is the third law of thermodynamics, which deals with absolute zero and entropy. This law states that as the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero (0 Kelvin), the entropy of the system approaches a minimum or zero value. This is crucial in the study of quantum mechanics and understanding the behavior of matter at extremely low temperatures.
Conclusion
In this overview of thermodynamics, we have explored the second and third laws, shedding light on the fundamental principles governing energy and matter in the universe. These laws are not just theoretical concepts; they have practical applications in our daily lives, from the design of efficient machines to the functioning of biological systems. Understanding the laws of thermodynamics allows us to make sense of the world around us and shape the technologies that power our modern society.