SIMULATION AND MODELING IN CIVIL ENGINEERING: PREDICTIVE ANALYSIS AND OPTIMIZATION OF STRUCTURAL DESIGNS AND PERFORMANCE
Simulation and modeling have emerged as powerful tools in the field of civil engineering, enabling engineers to predict and optimize the performance of structural designs. This article explores the role of simulation and modeling in civil engineering and its potential to enhance the efficiency, safety, and sustainability of infrastructure projects. We delve into the applications of simulation and modeling, including predictive analysis and optimization techniques, which play a crucial role in designing and evaluating structural systems. Furthermore, we discuss the benefits and challenges associated with these advanced computational methods and provide insights into their future prospects in the field of civil engineering.
- Introduction Civil engineering involves the design, construction, and maintenance of various infrastructure projects, such as buildings, bridges, dams, and highways. The complexity and scale of these projects require thorough analysis and evaluation to ensure their structural integrity, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Simulation and modeling techniques have revolutionized the way civil engineers approach these challenges by enabling them to simulate real-world scenarios and predict the behavior of structures under different conditions.
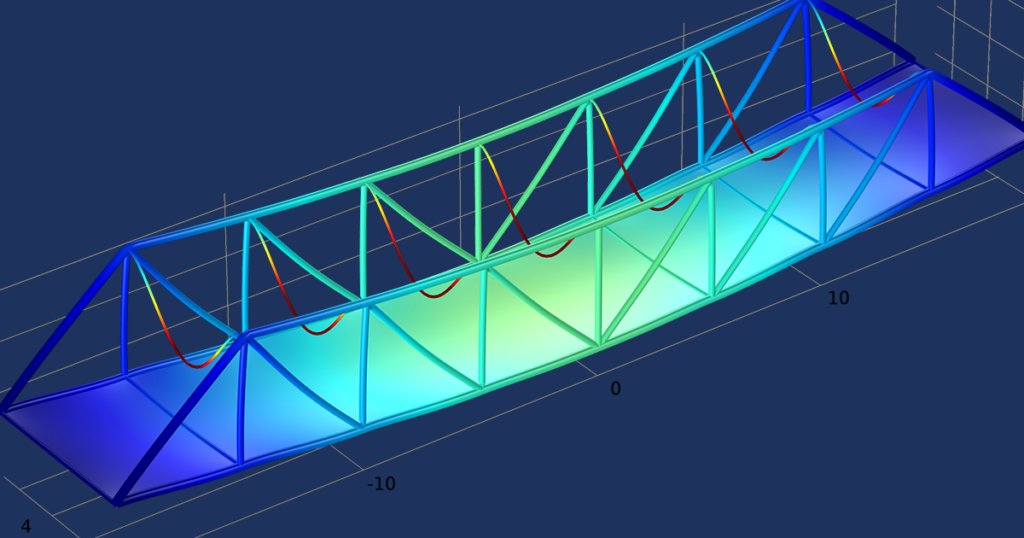
- Simulation and Modeling in Civil Engineering 2.1. Predictive Analysis Simulation and modeling allow civil engineers to analyze the behavior of structures before they are built or during their operational life. By creating virtual models and applying mathematical algorithms, engineers can simulate and predict the response of structures to various loads, such as gravity, wind, seismic forces, and traffic. This predictive analysis helps identify potential design flaws, optimize structural configurations, and assess the safety and performance of infrastructure projects.
2.2. Structural Design Optimization Simulation and modeling also facilitate structural design optimization, where engineers can explore different design alternatives and evaluate their performance to identify the most efficient and cost-effective solutions. By employing optimization algorithms and analyzing simulation results, engineers can iteratively refine structural designs, reducing material usage, minimizing environmental impact, and improving overall structural performance.
- Applications of Simulation and Modeling 3.1. Structural Analysis and Evaluation Simulation and modeling enable detailed structural analysis, allowing engineers to study the behavior of complex systems under different loading conditions. This includes analyzing the strength, stiffness, and stability of structural elements, as well as assessing the vulnerability to various hazards, such as earthquakes and extreme weather events. By accurately predicting the response of structures, engineers can optimize their designs and ensure the safety and resilience of infrastructure.
3.2. Construction Process Simulation Simulation and modeling techniques are also applied to simulate the construction process itself. Virtual construction models can be used to analyze construction sequences, simulate the behavior of construction equipment, and optimize construction schedules. This helps in identifying potential conflicts, improving construction efficiency, and reducing project delays and costs.
3.3. Material Behavior and Durability Simulation and modeling assist in understanding the behavior of construction materials, such as concrete, steel, and composites, under different environmental conditions. This knowledge aids in predicting material performance, including strength, deformation, and durability over time. By simulating the long-term behavior of materials, engineers can develop strategies for maintenance, repair, and rehabilitation of infrastructure, extending their lifespan and reducing lifecycle costs.
- Benefits and Challenges 4.1. Benefits of Simulation and Modeling
- Improved design accuracy and performance prediction.
- Reduced project costs by optimizing structural configurations and materials.
- Enhanced safety through detailed analysis of structural behavior under various conditions.
- Increased sustainability by minimizing material usage and environmental impact.
- Shortened design and construction cycles through iterative design refinement and process optimization.
4.2. Challenges of Simulation and Modeling
- High computational requirements and complexity of simulation models.
- Availability and accuracy of material and structural data for modeling.
- Integration of simulation tools with existing design and analysis workflows.
- Validation and verification of simulation models against real-world performance.
- Training and expertise required for effective utilization of simulation techniques.
- Future Prospects Simulation and modeling technologies in civil engineering are expected to continue advancing rapidly. With the advent of artificial intelligence and machine learning, engineers can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of simulations, enabling more reliable predictions and optimization. Integration with emerging technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Internet of Things (IoT) will further streamline the simulation process, facilitating real-time monitoring and control of structures. Moreover, the increasing availability of computational resources and cloud-based simulation platforms will make these techniques more accessible to engineers worldwide.
- Conclusion Simulation and modeling have revolutionized civil engineering by providing powerful tools for predictive analysis and optimization of structural designs and performance. Through these computational methods, engineers can accurately predict the behavior of structures, optimize designs, and enhance the safety, efficiency, and sustainability of infrastructure projects. Although challenges exist, ongoing advancements in technology and increased integration with other tools and technologies hold great promise for the future of simulation and modeling in civil engineering.